- Earn too little to qualify for subsidies to purchase coverage from the insurance marketplace and too much to qualify for traditional Medicaid;
- Are between the ages of 19 and 64 and are excluded from current Medicaid eligibility;
- Have an income at or below 138 percent of the federal poverty level, or approximately $17,000 for an individual or $35,000 for a family of four; and
- More than two-thirds of Nebraskans who fall in the coverage gap are employed.
- A greater percentage of Nebraskans who are employed but lack health insurance coverage reside in the state’s most rural counties: 12.32 percent compared to the state’s average of 11.42 percent.
The implementation of Medicaid expansion in the state currently rests with the Nebraska Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS). A timeline for enrollment has been set for October 2020 by DHHS—nearly two years after voters expanded coverage.
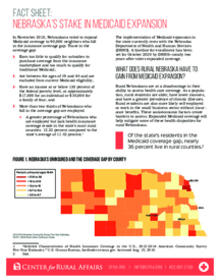
What does rural Nebraska have to gain from Medicaid expansion?
Rural Nebraskans are at a disadvantage in their ability to access health care coverage. As a population, rural residents are older, have lower incomes, and have a greater prevalence of chronic illnesses. Rural residents are also more likely self-employed or work in the small business sector without insurance benefits. These socioeconomic factors create barriers to access. Expanded Medicaid coverage will help mitigate some of these health disparities for rural Nebraskans.
The high percentage of uninsured rural residents has broad economic implications.
- Significant uncompensated care costs for hospitals and clinics.
- Concerns of hospital closures, and the associated loss of jobs and economic activity.
- More limited access to care for all rural residents.
- Increased insurance premiums for all residents.
Expansion benefits all Nebraskans
Medicaid expansion stands to grow the state’s economy and workforce, while improving the health of residents. These benefits are wide-ranging:
- Low-income households spend a greater share of annual income on health care than their wealthier counterparts. Nationally, health care spending accounts for 18.9 percent of annual income for the lowest income households. The wealthiest households spend only 3.9 percent of annual income on health care costs.
- Expansion will defer these health care costs for low-income residents, allowing them to spend more of their discretionary dollars in our local economies.
- Over three years, the federal share of expansion costs will stimulate more than $1.3 billion in economic activity across the state.
- This economic stimulus will support nearly 11,000 jobs annually.
- Medicaid expansion stands to reduce uncompensated care costs for Nebraska hospitals and clinics by nearly $343 million over a three-year period.
- Nearly 45 percent of the state’s 64 critical access hospitals are under financial stress. For many hospitals, the ability to provide services to Medicaid patients allows them to remain viable.
Adding jobs, stimulating economic activity, and preserving our rural hospitals increases quality of life for all Nebraskans. When our state’s economy does better and our communities are more vibrant, more Nebraskans are able to live the good life.